Your computer might look calm on the outside, but inside it’s a tiny furnace working nonstop. And understanding the cpu temperature range your processor operates within can mean the difference between silky-smooth performance and a sudden shutdown.
Most people never check their CPU temperature—until their PC starts lagging, freezing, or making suspicious fan noises. That’s when panic sets in. In reality, knowing what’s normal, what’s dangerous, and how to fix overheating can save you hundreds of dollars in hardware damage and years off your processor’s lifespan.
Whether you’re gaming, editing videos, coding, or just browsing the web, your processor generates heat constantly. The key isn’t eliminating heat—it’s keeping it within a safe cpu temperature range that ensures performance, stability, and longevity. Let’s break it down in simple, human terms.
What Is CPU Temperature and Why It Matters
What Is CPU Temperature?
CPU temperature refers to the internal heat level of your processor while it performs tasks. Every calculation—whether it’s loading a webpage or rendering a 4K video—produces thermal energy.
Modern processors from Intel and AMD are designed to handle heat efficiently. However, they operate within a specific cpu temperature range that ensures stable performance. Go beyond that, and you risk thermal throttling or hardware damage.
Why Temperature Impacts Performance
Heat directly affects:
- Processing speed
- System stability
- Component lifespan
- Energy efficiency
When temperatures rise too high, your CPU automatically slows down to prevent damage—a process called thermal throttling. That’s why your game suddenly drops from 120 FPS to 45 FPS without warning.
In extreme cases, systems shut down entirely to protect internal components.
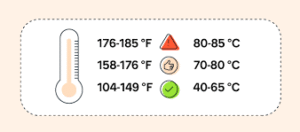
Ideal CPU Temperature Range Explained
Let’s define what “normal” really means.
The ideal <strong>cpu temperature range</strong> depends on workload, cooling system, and processor model. However, general safe benchmarks apply to most modern CPUs.
Normal Temperature Ranges
| Activity Level | Ideal Temperature Range |
|---|---|
| Idle | 30°C – 45°C |
| Light Usage | 40°C – 55°C |
| Gaming / Heavy Tasks | 60°C – 80°C |
| Maximum Safe Limit | 85°C – 95°C |
Most CPUs have a maximum junction temperature (Tj Max) between 95°C and 105°C. Crossing this repeatedly shortens lifespan significantly.
What’s Considered Dangerous?
- Sustained temps above 90°C
- Sudden spikes beyond 100°C
- Frequent shutdowns due to heat
If your CPU regularly exceeds the safe cpu temperature range, immediate cooling improvements are necessary.
CPU Temperature Range for Different Activities
Not all workloads are created equal. Streaming Netflix is very different from rendering 3D animation.
Idle Temperature
When your system is sitting at the desktop:
- Ideal: 30–45°C
- Slightly warm rooms may push this to 50°C
If idle temps exceed 60°C, something’s wrong—likely dust buildup or poor thermal paste application.
Gaming
Gaming pushes CPUs hard, especially in open-world or competitive titles.
- Expected cpu temperature range: 60–80°C
- Brief spikes up to 85°C are acceptable
However, consistent temps above 90°C indicate airflow issues.
Video Editing & Rendering
Creative professionals experience heavy CPU usage:
- Safe operating range: 70–85°C
- Proper cooling becomes essential
Interestingly, high-end CPUs like the Intel i9 or Ryzen 9 often run warmer due to increased core counts.
Overclocking
Overclocking increases clock speed—and heat.
- Recommended maximum: 85–90°C under load
- Above 90°C reduces stability
Overclockers must invest in liquid cooling or premium air coolers.
What Causes High CPU Temperatures?
Understanding the cause is half the solution.
Common Reasons for Overheating
- Dust-clogged fans
- Poor case airflow
- Old or poorly applied thermal paste
- Inadequate CPU cooler
- High ambient room temperature
- Overclocking without sufficient cooling
I once helped a friend whose PC kept crashing during gaming. Turns out, his case fans were installed backward. Air wasn’t flowing—it was trapped. Fixing that alone reduced his cpu temperature range by nearly 12°C.
How to Check Your CPU Temperature
Monitoring is simple and free.
Built-in BIOS Monitoring
Restart your PC and enter BIOS/UEFI. Most motherboards display CPU temperature in real-time.
Software Tools
Popular tools include:
- HWMonitor
- Core Temp
- MSI Afterburner
- NZXT CAM
These apps provide real-time temperature graphs and alert you if your cpu temperature range crosses safe limits.
Safe CPU Temperature Range for Gaming and Overclocking
Gamers care deeply about temperature because performance equals competitiveness.
A well-cooled gaming PC should maintain:
- 65–75°C during intense gameplay
- Brief spikes under 85°C
For overclocking:
- Stay under 90°C
- Ensure voltage settings are stable
Professional eSports setups often use liquid cooling systems to maintain optimal cpu temperature range under sustained load.
Laptop vs Desktop CPU Temperature Range Differences
Laptops run hotter—period.
Why Laptops Heat More
- Compact design
- Limited airflow
- Shared cooling between CPU and GPU
Typical laptop cpu temperature range:
- Idle: 40–55°C
- Load: 75–95°C
While 90°C on a desktop is alarming, it’s more common on gaming laptops. Still, sustained high temps reduce battery and hardware longevity.
How to Lower CPU Temperature Effectively
Cooling doesn’t have to be expensive.
Quick Fixes
- Clean dust with compressed air
- Reapply thermal paste (every 2–3 years)
- Improve cable management
- Adjust fan curves in BIOS
Advanced Solutions
- Upgrade to a tower air cooler
- Install AIO liquid cooling
- Add more intake/exhaust fans
- Use high-quality thermal paste (e.g., Arctic MX-6)
Even lowering your cpu temperature range by 5°C can significantly extend processor lifespan.
Long-Term Effects of Overheating
Heat is the silent killer of electronics.
Potential Damage Includes:
- Reduced silicon lifespan
- Motherboard VRM stress
- Thermal throttling
- Random system crashes
- Data corruption
According to semiconductor reliability studies, every 10°C increase above optimal temperature can halve component lifespan. That’s significant.
Keeping your cpu temperature range stable protects your investment long-term.
Personal Background: Why CPU Cooling Became My Obsession
I didn’t start as a hardware enthusiast. Years ago, I lost an expensive workstation to overheating during a 3D rendering project. The motherboard failed, and I lost weeks of work.
That painful lesson pushed me into studying thermals, airflow physics, and hardware optimization. Since then, I’ve built over 70 custom PCs for gamers, editors, and developers. Some of those builds run 24/7 for streaming setups generating six-figure annual incomes.
Financially speaking, investing $100 in proper cooling can protect $1,000+ worth of components. From a cost-benefit perspective, thermal management has one of the highest returns in PC building.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the normal cpu temperature range?
For most systems, 30–45°C at idle and 60–80°C under load is considered safe.
Is 90°C too hot for a CPU?
Yes, sustained 90°C is risky. Occasional spikes may be acceptable, but consistent operation at that level shortens lifespan.
Why does my CPU overheat even with a good cooler?
Possible reasons include poor thermal paste application, restricted airflow, or high ambient room temperature.
Does gaming damage the CPU?
Not if the cpu temperature range remains within safe limits. Modern CPUs are designed for heavy workloads.
How often should I replace thermal paste?
Every 2–3 years for optimal heat transfer.
What happens if CPU temperature reaches 100°C?
Most systems shut down automatically to prevent permanent damage.
Do AMD CPUs run hotter than Intel?
Not necessarily. Both brands operate within similar thermal limits depending on architecture.
Can high CPU temperature affect FPS?
Absolutely. Thermal throttling reduces clock speeds, lowering frame rates.
Conclusion
Your processor works tirelessly every second your computer is on. Treating it well by maintaining a healthy cpu temperature range isn’t just good practice—it’s essential for performance, stability, and long-term reliability.
Whether you’re a casual user or a hardcore gamer, monitoring temperatures and improving airflow can dramatically improve your system’s lifespan. A cool CPU is a happy CPU—and a happy CPU means fewer crashes, smoother gameplay, and peace of mind every time you hit the power button.